Written by Nadia Saffarian
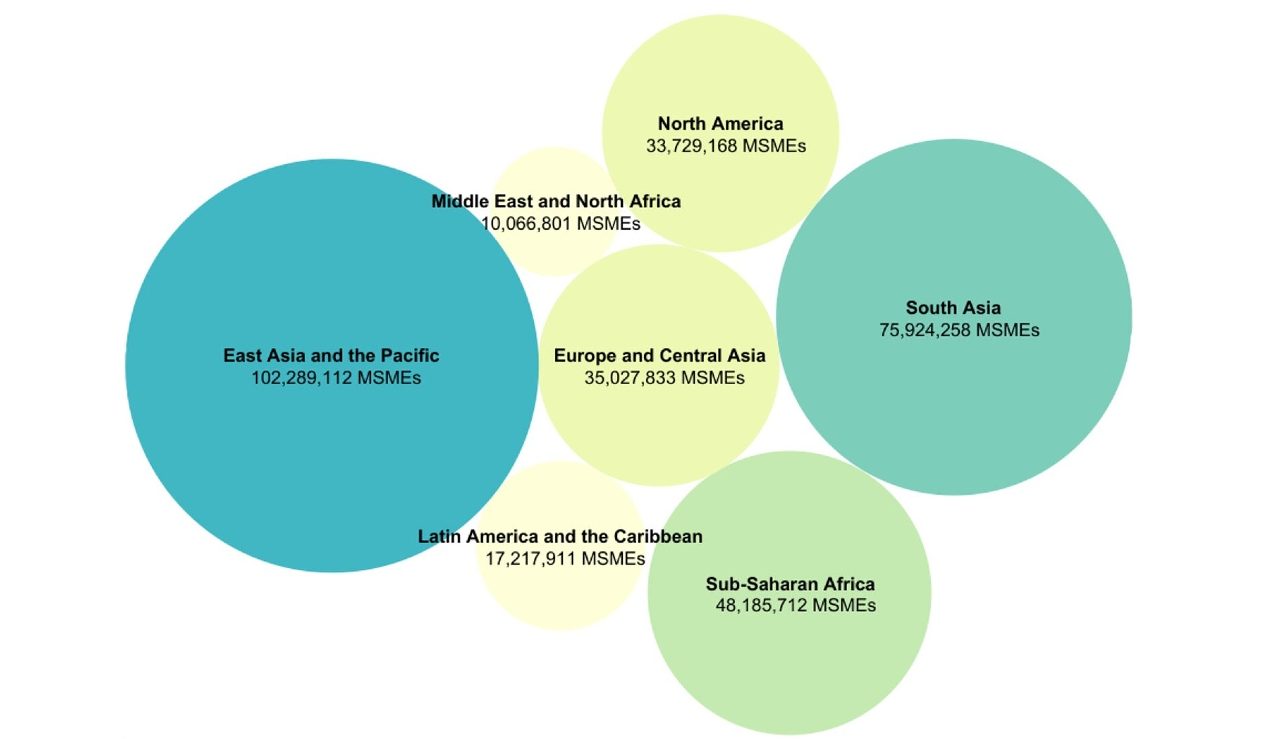
According to the International Finance Corporation (IFC), 40% of micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in developing countries have unmet financing needs. This amounts to $5.2 trillion every year, the equivalent of 1.4 times the current level of global MSME lending. Since MSMEs are the principal engines of job creation and economic growth worldwide, accounting for more than two-thirds of global employment opportunities, it is crucial that this constraint is relieved in order to advance economic development, enable higher growth, and reduce poverty.
The need to eliminate the finance gap is particularly acute in emerging markets, where MSMEs are responsible for 70% of job opportunities. How will these emerging countries continue generating employment opportunities if these businesses lack the finance required to grow? With the current MSME finance gap, this just doesn’t look achievable. CEO of Opportunity Network, Brian Pallas, shares his vision on how digitalization can help close this gap.
Opportunity Network is a private digital network that connects CEOs and investors to reliable counterparts worldwide for all their commercial, investing, fundraising, and merger and acquisition needs. There are no intermediaries, nor commissions taken for any business generated, and all members are vetted by the network’s partner institutions, which include Boston Consulting Group, Citizens Bank, The London Stock Exchange, and Young Presidents’ Organization, among others.
But in order to ensure widespread benefit from these solutions, MSME owners and policymakers have a responsibility to empower these businesses’ employees by building their trust in technology and enhancing their digital skills.
Digitalization as an enabler of MSME Finance
Digitization can be a game-changer for MSME financing. The rising use of mobile phones in emerging countries is increasing the availability of digital financial services for MSMEs, while digital financial products and advanced data analytics are helping these largely informal businesses build a credit history, opening the door to formal financing.
Digital payroll systems and forms of identification also enable informal organizations to register and operate formally, as well as to fulfill regulatory requirements for customer identification and verification. Additionally, digital platforms are offering entrepreneurs access to a universe of global financing opportunities that they wouldn’t have had access to otherwise.
The digital transformation of MSMEs also lowers transaction costs for the lenders and banks that serve them. The greater their digital footprint, the more MSMEs appeal to technology-focused alternative SME lenders that can use data to decrease the costs related to loan origination and collection, thereby increasing the profitability of serving the MSME market. More traditional lenders like banks can also benefit from advances in analytic and processing capabilities, which fuel data-driven intelligence that can inform their initial decision-making and portfolio management.
Key MSME lending technologies and their impact
There are a number of key digital technologies that are increasing MSMEs’ access to finance. I’ll discuss a few of them below.
Digital platforms are essential for MSMEs looking to establish a digital presence, as they offer consumers and businesses the ability to connect to financial and other service providers through an online or mobile channel as an integrated part of their day-to-day activities. They significantly increase the network capacity of these enterprises, as well as the number of suppliers, clients, investors, and business opportunities they can reach. Many digitally-enabled online services can even help companies reduce both the time and money spent on the implementation of digital business processes, as well as the collection and management of data.
At Opportunity Network, we’ve seen a huge shift as business leaders have increasingly turned to online platforms as a means of sourcing financing and investment opportunities. Since the pandemic began, over 10,000 new companies have joined our digital business matching network. As a result, we’ve seen a 70% increase in conversations among members and a 60% growth in the number of new business opportunities posted.
We are now able to match 70% of deals with at least four counterparts in just 48 hours. The platform now hosts a $400 billion transaction flow, drawing participation from over 45,000 C-level executives and private investors across more than 100 industries and over 130 different countries.
Blockchain is also a key technology in MSME finance, and it can help financial service providers better target these businesses in a number of ways, for instance:
- by allowing MSMEs to provide a concrete record of verified identity credentials for customer identification and verification;
- by allowing MSMEs to be more transparent about their credit history, since their borrowing activities are performed on a public ledger, thereby minimizing loan risk;
- by enhancing trade finance through greater interaction and information-sharing between participants from different industries and countries, provided in a verifiable and decentralized manner;
- by providing a single mechanism that can track several parts of the trade finance process, including orders, contracts, documentation, shipments, customs and delivery;
- by decentralizing capital markets and providing automated settlement and custody solutions, increasing access and reducing financing costs for MSMEs.
Examples of blockchain-based solutions for MSMEs include AliPay, the largest digital payments platform in the world, and Visa B2B Connect, an enterprise blockchain infrastructure that facilitates global financial transactions for corporate clients.

Artificial intelligence and machine learning are important technologies in MSME lending, as they allow MSMEs and other businesses to extract value from the extensive volume of information found in the databases of traders, banks, logistics companies, and others. This data can be algorithmically predictive in governing risk management – a key part of unlocking MSME finance. Credit scoring models using artificial intelligence and machine learning also allow MSMEs with no previous access to finance to be served. Similar to Big Data analytics, these technologies have the potential to pinpoint money laundering and anticipate fraud in a more accurate and efficient manner. Therefore, they can also strengthen companies’ ability to comply with AML/CFT regulations, while minimizing compliance costs and fraud losses.
Examples of these technologies’ applications include Ant Financial’s artificial intelligence/machine learning-enabled credit scoring in East Asia, M-Shwari in East Africa, M-Kajy in Madagascar, and MoMo Kash in Côte d’Ivoire. M-Shwari, for example, uses machine learning to anticipate the likelihood of borrowers defaulting on payments in the future. As a result, it was able to deliver small loans to 21 million Kenyans by the end of 2017.
Open APIs are also a key MSME finance technology, as they have enabled the open banking movement that is revolutionizing the financial services sector. This approach allows for the communication and exchange of data between different platforms, such as banks or fintechs, enabling them to better leverage their data in order to offer personalized digital products and services to MSMEs. Open APIs also provide credible digital identity solutions for customer verification/identification, and for authorizing access to the customer’s account.
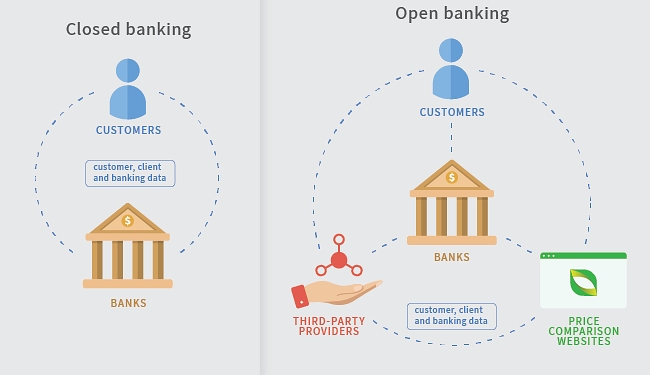
Examples include:
- Absa Group, which fosters a pan-African financial services marketplace that delivers banking as a service to all, including low-income households.
- Wave Money in Myanmar, which enables fintechs and others to easily incorporate seamless digital payment capabilities into their online businesses in a low-banked, high-smartphone penetration market.
- BTPN in Indonesia, whose mission is to optimize their agent network and create new revenue streams using open API-enabled strategic partnerships.
- MTN in Uganda, which drives customer growth and activity by using open APIs to broaden the range of mobile wallet applications available to customers.
Closing the MSME digital gap
Although these technologies have the potential to close the MSME finance gap in emerging economies, the broader MSME digital gap continues to slow productivity growth and increase inequalities among people, organizations, and locations. Lack of awareness among MSME owners about the possibilities offered by digital technology is hindering diffusion, and lack of access to digital infrastructures and business practices is making it difficult for these enterprises to undergo digital transformation.
Business leaders and policymakers can help remove these obstacles by:
- Investing in digital skills training, organizational change, process innovation, and new systems and business models;
- Designing or informing policies that shape conducive framework conditions and remove obstacles to MSME digitization;
- Promoting knowledge-sharing and learning about the ways in which MSMEs in different sectors can reap the benefits of digitization, as well as about the role of governments, regulators, businesses and other institutions in encouraging MSME digitization;
- Finding solutions to the lack of internet access and poor digital infrastructures in emerging markets.
These and other efforts are necessary to bring the full benefits of digital technology to MSMEs and their customers and communities in developing countries. If this digital transformation is successful, these essential businesses will not only enjoy greater access to finance, they’ll significantly increase their ability to advance economic development and reduce poverty around the world.
Photo courtesy of Mira Gratier/DFID.




